Piles, also known as hemorrhoids, are lumps that form inside and around the anus. They can cause symptoms like itchiness, discomfort, pain, and rectal bleeding.
Piles affect both men and women. However, women have more risk factors. These include pregnancy, hormonal changes, and lifestyle habits. This is why it is important to know what causes piles in females and how to prevent them from happening.
Embarrassment and lack of knowledge prevent many women from seeking help. A good understanding of symptoms, diagnosis, prevention, and natural cures allows people to treat piles successfully. You can do this without worrying about them coming back.
A mix of physical changes, hormones, and lifestyle factors causes piles in women and affects their bodies. Some of the frequent causes of piles in women include:
1. Pregnancy and Childbirth
During pregnancy, the expanding uterus exerts pressure on pelvic veins and hormonal changes cause digestion to be sluggish. And both those factors promote piles. Straining during the delivery can also worsen- swollen veins, eventually making new mothers prone to piles.
2. Hormonal Changes
Hormonal changes during menstrual cycles, pregnancy and menopause can impact bowel habits and blood vessel health. When progesterone levels go up, digestion slows. This can cause constipation.
Low estrogen makes vein walls more likely to swell. These modifications predispose ladies to piles at various phases of life.
3. Chronic Constipation
The chronic constipation makes women strain, which exerts pressure to the rectum veins. This pressure damages the tissues and painful swelling occurs as a result. Low-fiber diets, dehydration and some medications tend to make the problem worse.
4. Sedentary Lifestyle
Sitting for long hours at work, while studying, or even during household routines reduces circulation in the pelvic area. This stagnant blood flow increases pressure on rectal veins. Over time, it contributes to the development of piles in women.
5. Obesity
The abdomen and pelvis are constantly strained under the burden of excess body weight. The additional pressure affects the veins around the anus, causing them to be more likely to swell. Obesity increases the chances of developing constipation, which in turn aggravates piles.
6. Poor Diet
Overeating processed, refined and hot foods may lead to indigestion and constipation. Insufficient fiber in the diet causes stools to harden and become more difficult to pass. This causes strain, which is the direct cause of or exacerbating factor for piles.
7. Genetics
Hereditary is a strong factor in the development of piles. Those with genetically weaker vein walls or poor vascular support are naturally more susceptible. In those situations, even the mild constipation induces so much of pressure that causes swollen veins in rectum.
8. Chronic Coughing
Ailments such as asthma, bronchitis or recurring respiratory infections keep the abdominal muscles constantly tight. Excessive coughing puts stress on the rectal veins which then become weak with time. This may be one reason piles are more likely to develop or to get worse in women who have long-term cough.
9. Heavy Lifting
Women who exercise a lot, have tough jobs, or lift heavy things at home can strain their pelvic muscles without knowing. This pressure boosts intra-abdominal strain that will bring about the particular swelling associated with rectal veins. If its constant over time, it can cause piles.”
10. Postpartum Recovery
Postpartum constipation is common in women following childbirth as a result of hormonal changes, medication use and physical immobility. The pressure from having a baby also causes postpartum piles to be common. Early treatment with lifestyle modifications is essential for recovery.
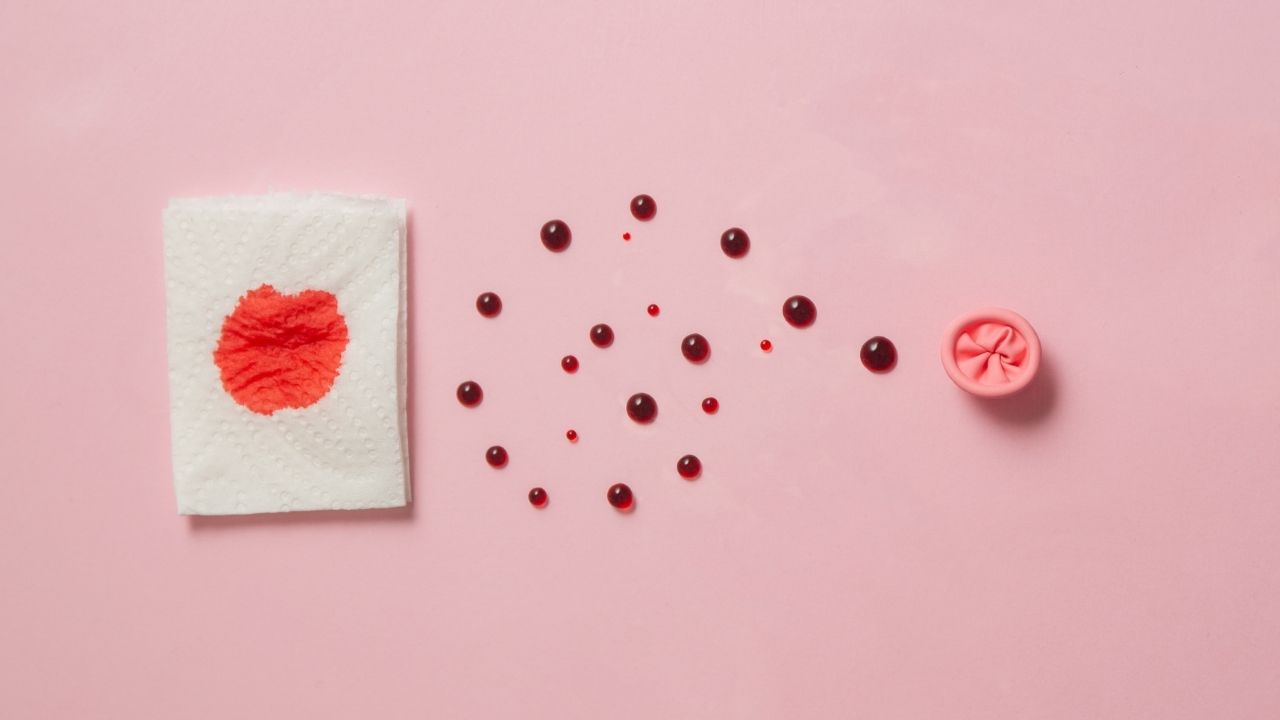

What are the Symptoms of Piles in Female?
It is important to know if you have piles early on. This helps you get treatment on time and avoid future problems. The symptoms or piles in women vary and are either internal and external. Common symptoms of piles in female include:
Rectal Bleeding
One of the salient features of piles. This may show up as bright red blood on toilet paper, in the stool or in the toilet bowl.
Unlike other diseases of the digestive system, piles bleeding is red fresh and painless (most often in internal piles).
Pain and Discomfort
Women often feel sharp or throbbing pain while sitting for long hours, cycling, or during bowel movements.
Pain tends to worsen in external or thrombosed piles.
Itching or Irritation Around the Anus
Swelling and mucus discharge may irritate the skin around the anus, causing constant itching.
This may also lead to hygiene-related issues.
Swelling or Lump Formation
Small lumps may develop near the anus, which can be tender and painful to touch.
In prolapsed piles, the lump may protrude outside the anal canal.
Incomplete Bowel Evacuation
Women often report feeling as if their bowel hasn’t fully emptied even after passing stools.
Mucus Discharge
Some women notice a clear or yellow discharge after bowel movements, often accompanied by irritation.
Important Note: Women often confuse these symptoms with those of a urinary tract infection (UTI). They may also mistake them for other gynecologic issues. A delay in diagnosing piles can even make it worse. Therefore, early warning sounds are crucial.

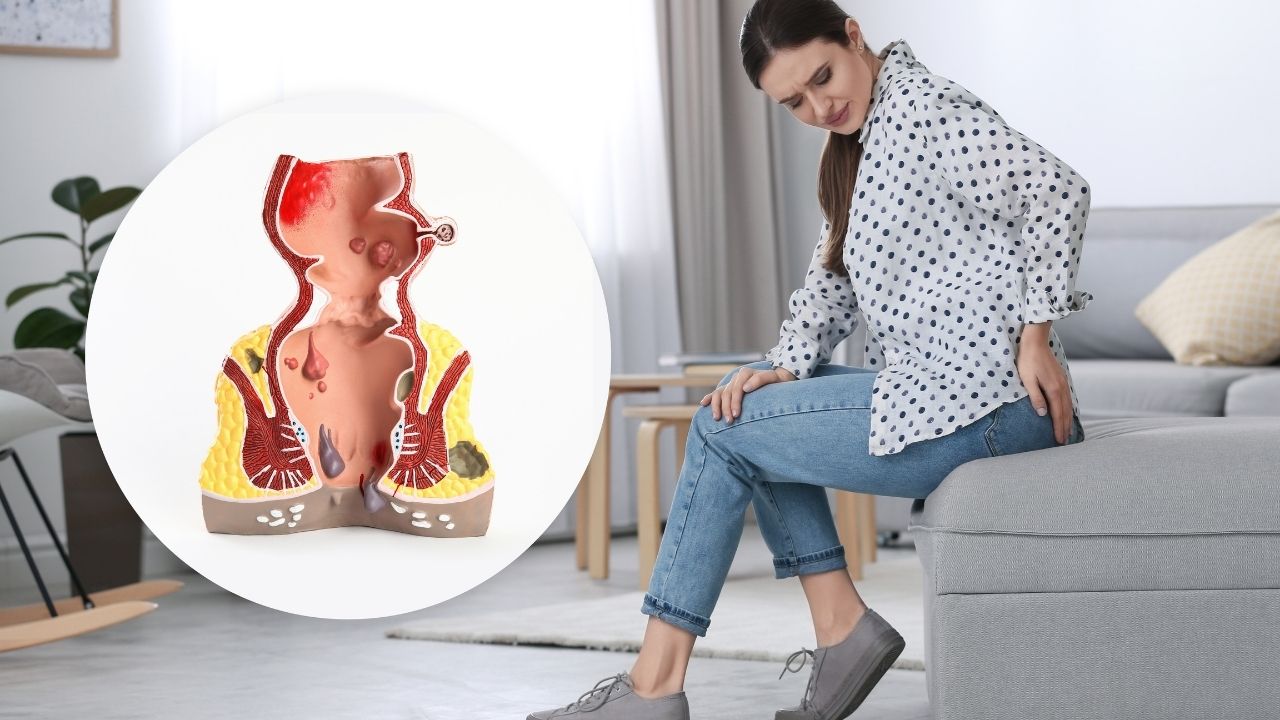
Different Types of Piles in Female
Piles can be classified into four types which are characterized by different symptoms and severity. Knowing about these types, helps women recognize what stage they may be in, and seek the appropriate treatment. Different types of piles in female include:
1. Internal Piles
It is located inside the rectum and cannot be seen from outside.
It is typically painless because of fewer nerve endings, but it may cause rectal bleeding.
It is more severe in some cases, that it can become so large that they protrude from the anus, which can be excruciatingly painful.
2. External Piles
It grows under the skin near the opening of the anus.
It’s painful, itchy and can be miserably uncomfortable.
The woman may feel a hard lump if she strains out during bowel movements.
3. Prolapsed Piles
Hemorrhoids that are forced out of the anus by straining.
Retract automatically, and you can push it back manually.
In more severe cases it may require medical or surgical management.
4. Thrombosed Piles
External hemorrhoids in which there are clots around swollen veins.
Very painful, with swelling, tenderness and bluish discoloration of the affected area.
Important Note: Pregnancy and delivery are the most common reasons for prolapsed and thrombosed piles in women. Knowing these types helps a woman understand her condition. She can determine whether she has the mildest form, which is internal, or the most serious form, which is prolapsed or thrombosed.

How Piles is Diagnosed in Women
Diagnosing piles in women can be difficult. This is because the symptoms can be similar to other conditions. These include anal fissures, fistulas, polyps, or colorectal cancer. A systematic method is essential for the accurate diagnosis of piles in women. Some of them include:
1. Medical History
Doctors ask about symptoms, bowel habits, diet, fluid intake, pregnancy history and family history.
This may eliminate other gynecological or digestive conditions.
2. Physical Examination
Anus is inspected for external swelling, lumps and prolapsed piles.
In women, a pelvic exam also may be recommended if symptoms overlap with gynecologic complaints.
3. Digital Rectal Examination (DRE)
Gloved, lubricated finger is placed inside the rectum to check for swelling, lumps or tenderness.
4. Anoscopy / Proctoscopy
The internal piles are examined with a small tube which contains light.
Aids to confirm the size, location and severity of the piles.
5. Colonoscopy / Sigmoidoscopy
Recommended if there is severe or persistent rectal bleeding, accompanied by unexplained weight loss.
Needed in women over 40 to prevent colorectal cancer.

How Piles Can Be Prevented in Women
The best way to avoid piles is to stop them from ever occurring in the first place. Modest changes in lifestyle can lower the risk greatly, particularly among women who are prone to constipation or pregnant. Pi;es can be prevented by considering certain factors such as:
1. Adopt a High-Fiber Diet
Include plenty of leafy greens, fruits, beans and whole grains.
The fiber loosens stool and makes bowel movements less strained.
Fiber in the diet of women who are on a weight loss diet should definitely not be set aside.
2. Stay Hydrated
It is recommended that you drink 8-10 glasses of water a day which aids in avoiding constipation.
Herbal teas, as well as soups also aids digestion.
3. Avoid Prolonged Sitting
Working women, and housewives have to sit for hours on chair which causes more pressure on rectum.
Taking short breaks to stretch or walk.
4. Exercise Regularly
Yoga poses such as Malasana (Garland Pose) and Pavanmuktasana (Wind Relieving Pose) promote intestinal health.
Gentle exercise helps to maintain circulation and lessens venous pressure.
5. Maintain Healthy Toilet Habits
Avoid straining during bowel movements.
Answer the natural call for stool passing without delay.
Spend less time in the toilet (No reading, scrolling on the phone or doing crossword puzzles while you’re there.)
6. Pregnancy Care
Pregnant women should consult their doctor about stool softeners, safe forms of physical activity, and dietary changes.
Bowel functioning and circulation are helped by regular walks during pregnancy.
Note for women: Preventive care is especially important during menstrual periods, pregnancy and the postpartum period when constipation occurs more frequently.

How to Treat Piles Naturally at Home
For light or early stages, treatment does not involve surgery and is completely curable. Natural treatment and lifestyle changes bring substantial relief. Some of the significant natural home remedies include:
1. Warm Sitz Baths
The patient should sit in warm water for 15–20 min twice daily, which diminishes itching, swelling and pain.
You can add Epsom salt for a more calming remedy.
2. Cold Compresses
Applying ice pack to the anal area can also help shrink swollen veins.
3. Aloe Vera
The natural anti-inflammatory gel that instantly relieves burning, itching.
Apply externally for quick relief.
4. Witch Hazel
A natural astringent that helps relieve itching, burning and swelling.
Available in wipes and ointments.
5 Isabgol and Flax Seeds
Increase stool bulk and make it easier to pass.
To reduce puffing, this should be ingested with enough water.
6. Healthy Lifestyle Changes
Don’t consume processed foods and too much caffeine or alcohol, which can exacerbate constipation.
Walking every day is beneficial for bowel movements.
7. Proper Hygiene
Wash your anal area with mild, unperfumed wipes or warm water.
Avoid soaps that are too harsh and rough toilet paper.
Important Note: These home remedies works for mild piles, if your system is persistent and symptoms are severe please seek medical advice. If necessary, doctors may suggest non-surgical treatments such as rubber band ligation or advanced surgical techniques.
Conclusion
Pregnancy, hormonal changes, diet, obesity, and a lack of exercise contribute to the development of piles in women. It is important to diagnose hemorrhoids early. Understanding the different types can help prevent serious damage.
Taking preventive steps can help reduce the risk of piles in women.
These steps include:
– Eating a high-fiber diet
– Staying hydrated
– Exercising
– Maintaining good toilet habits Other natural treatments include sitz baths, aloe vera and fiber supplements.
Piles affects many women around the world. Early medical help can treat the condition well. This can prevent complications and help women live healthier, more comfortable lives.